-
适用于 ERM 和 LRA 且具有内部存储器和智能环路架构的 DRV2604 触觉驱动器
- 1 特性
- 2 应用
- 3 说明
- 4 修订历史记录
- 5 Pin Configuration and Functions
- 6 Specifications
-
7 Detailed Description
- 7.1 Overview
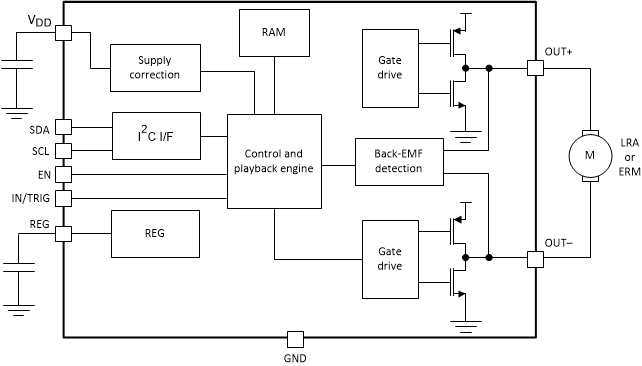
- 7.2 Functional Block Diagram
- 7.3
Feature Description
- 7.3.1 Support for ERM and LRA Actuators
- 7.3.2 Smart-Loop Architecture
- 7.3.3 Open-Loop Operation for LRA
- 7.3.4 Open-Loop Operation for ERM
- 7.3.5 Flexible Front-End Interface
- 7.3.6 Edge Rate Control
- 7.3.7 Constant Vibration Strength
- 7.3.8 Battery Voltage Reporting
- 7.3.9 One-Time Programmable (OTP) Memory for Configuration
- 7.3.10 Low-Power Standby
- 7.3.11 Device Protection
- 7.4 Device Functional Modes
- 7.5
Programming
- 7.5.1 Auto-Resonance Engine Programming for the LRA
- 7.5.2 Automatic-Level Calibration Programming
- 7.5.3 I2C Interface
- 7.5.4 Programming for Open-Loop Operation
- 7.5.5 Programming for Closed-Loop Operation
- 7.5.6 Auto Calibration Procedure
- 7.5.7 Programming On-Chip OTP Memory
- 7.5.8 Waveform Playback Programming
- 7.6
Register Map
- 7.6.1 Status (Address: 0x00)
- 7.6.2 Mode (Address: 0x01)
- 7.6.3 Real-Time Playback Input (Address: 0x02)
- 7.6.4 HI_Z (Address: 0x03)
- 7.6.5 Waveform Sequencer (Address: 0x04 to 0x0B)
- 7.6.6 GO (Address: 0x0C)
- 7.6.7 Overdrive Time Offset (Address: 0x0D)
- 7.6.8 Sustain Time Offset, Positive (Address: 0x0E)
- 7.6.9 Sustain Time Offset, Negative (Address: 0x0F)
- 7.6.10 Brake Time Offset (Address: 0x10)
- 7.6.11 Rated Voltage (Address: 0x16)
- 7.6.12 Overdrive Clamp Voltage (Address: 0x17)
- 7.6.13 Auto-Calibration Compensation Result (Address: 0x18)
- 7.6.14 Auto-Calibration Back-EMF Result (Address: 0x19)
- 7.6.15 Feedback Control (Address: 0x1A)
- 7.6.16 Control1 (Address: 0x1B)
- 7.6.17 Control2 (Address: 0x1C)
- 7.6.18 Control3 (Address: 0x1D)
- 7.6.19 Control4 (Address: 0x1E)
- 7.6.20 V(BAT) Voltage Monitor (Address: 0x21)
- 7.6.21 LRA Resonance Period (Address: 0x22)
- 7.6.22 RAM-Address Upper Byte (Address: 0xFD)
- 7.6.23 RAM-Address Lower Byte (Address: 0xFE)
- 7.6.24 RAM Data Byte (Address: 0xFF)
- 8 Application and Implementation
- 9 Power Supply Recommendations
- 10Layout
- 11器件和文档支持
- 12机械、封装和可订购信息
- 重要声明
DATA SHEET
适用于 ERM 和 LRA 且具有内部存储器和智能环路架构的 DRV2604 触觉驱动器
本资源的原文使用英文撰写。 为方便起见,TI 提供了译文;由于翻译过程中可能使用了自动化工具,TI 不保证译文的准确性。 为确认准确性,请务必访问 ti.com 参考最新的英文版本(控制文档)。
1 特性
- 灵活触控反馈/Vibra 驱动程序
- LRA(线性谐振致动器)
- ERM(偏轴转动惯量)
- 由 I2C 控制的数字回放引擎
- 用于存储波形的内部 RAM
- 通过 I2C 实现的实时回放模式
- 智能环路架构(1)
- 自动过驱/刹车 (ERM/LRA)
- 自动共振跟踪 (LRA)
- 自动传动器诊断 (ERM/LRA)
- 自动水平校准 (ERM/LRA)
- Immersion TouchSense®3000 兼容
- 占空比控制范围介于 0% 至 100% 之间的可选脉宽调制 (PWM) 输入
- 可选模拟输入控制
- 可选硬件触发引脚
- 高效输出驱动
- 快速启动时间
- 电源电压上的持续加速
- 兼容 1.8V 电压的 VDD 耐压数字引脚 (1)
1. 正在申请专利的控制算法
2 应用
- 手机
- 平板电脑
3 说明
根据设计,DRV2604 可在一条共用 I2C 兼容总线上对 ERM 和 LRA 传动器进行极其灵活的触觉控制。该控制使得主机处理器无需再生成脉宽调制 (PWM) 驱动信号,从而节省了成本高昂的计时器中断和硬件引脚。
DRV2604 器件包含足够的集成 RAM,从而允许用户预先加载超过 100 个的定制波形。可以通过 I2C 即时回放这些波形,也可以选择通过硬件触发引脚来触发这些波形。此外,主机处理器可利用实时回放模式旁路掉库回放引擎并通过 I2C 从主机直接播放波形。
DRV2604 器件还包含一个智能环路架构,该架构可实现针对 LRA 的轻松自动谐振驱动以及优化反馈的 ERM 驱动。这种反馈提供了自动过驱和制动,进而形成简化的输入波形范式并实现可靠电机控制和持续电机性能。
DRV2604 器件 具有 一个经三重调制的输出级,从而能够提供比基于线性的输出驱动器更高的效率。DRV2604 器件采用 9 焊球 WCSP 封装,具有很少的组件数量,操作灵活,是支持触控的便携式振动和触觉应用的理想 选择。
器件信息(1)
| 器件型号 | 封装 | 封装尺寸(最大值) |
|---|---|---|
| DRV2604 | DSBGA (9) | 1.50mm x 1.50mm |
- 如需了解所有可用封装,请参阅数据表末尾的可订购产品附录。
4 修订历史记录
Changes from B Revision (December 2015) to C Revision
- Changed the DEFAULT value for bit 5-4 of Table 19 From: 1 To 3 Go
- Changed the DEFAULT value for bit 3-2 of Table 19 From: 2 To 1 Go
- Changed the DEFAULT value for bit 1-0 of Table 19 From: 2 To 1 Go
- Changed the typical value of C(VDD) in Table 27 From: 0.1 µF To: 1 µFGo
- Changed the input-voltage supply range From: 2 V to 5.2 V To: 2.5 V to 5.5 V in the Power Supply Recommendations sectonGo
Changes from A Revision (July 2015) to B Revision
- Changed th(1) Hold time, SCL to SDA from 10 ns to 50 ns in Timing RequirementsGo
- Changed the default value of NG_THRESH[1:0] from 1 to 2 in the Register MapGo
Changes from * Revision (December 2012) to A Revision
- Added 添加了特性项目 Immersion TouchSense 3000 兼容Go
- 根据新的数据表样式更新了文档Go
- 完整规格版本 Go
- Changed 更改了简化原理图 Go
- Changed minimum supported resonant frequency from 50 Hz to 125 Hz Go
- Added digital pulldown resistance parameter to Electrical CharacteristicsGo
- Changed calibration diagram to include DRIVE_TIME into ERM requirementsGo
- Changed bitfield name from "LRA_DRIVE_MODE" to "OTP_STATUS"Go